The post below will show how to disable fair sharing of CPU, disk and network in Windows Server 2012/2012R2. The post relies on information found in here and here.
It’s possible to disable it directly in the Windows Registry with the program RegEdit.exe or using PowerShell commands. Both approaches will be shown.
Disclaimer: Do a backup of Windows Registry in RegEdit.exe (File -> Export, remember to choose Export Range = All) before doing these changes!
It’s possible to disable fair sharing of the CPU using Regedit.exe. You have to change the value EnableCPUQuota from 1 to 0 (zero). NB! You change it by double-clicking on EnableCpuQuota. This value can be found in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Quota System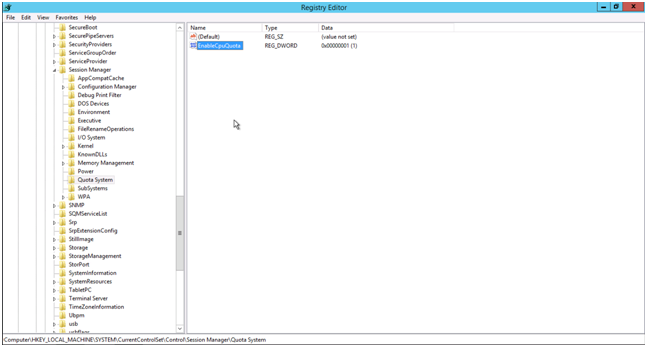
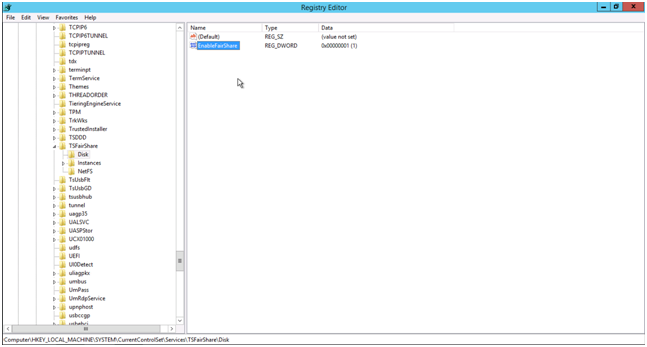
It’s possible to disable fair sharing of the disk using Regedit.exe. You have to change the value EnableFairShare from 1 to 0 (zero). This value can be found in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TSFairShare\Disk
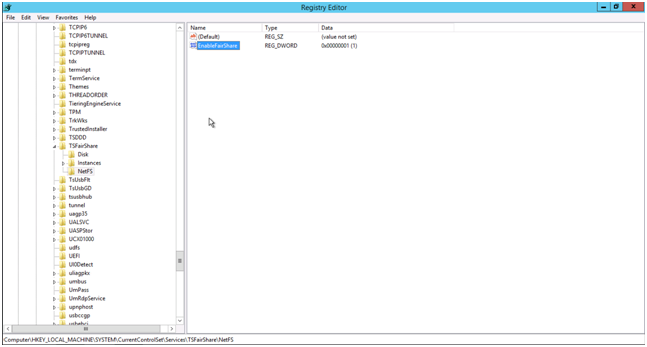
It’s possible to disable fair sharing of the network using Regedit.exe. You have to change the value EnableFairShare from 1 to 0 (zero). This value can be found in
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\TSFairShare\NetFS
It is also possible to do this through PowerShell where you write the command below
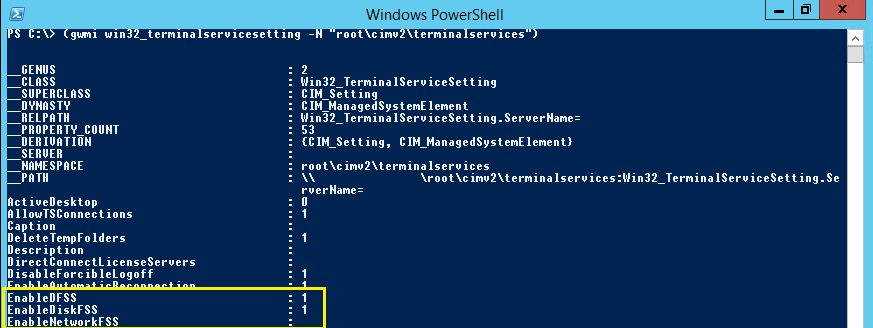
(gwmi win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices")
This will give you a list of the settings for terminalservices as shown below. You are interested in EnableDFSS, EnableDiskFSS and EnableNetworkFSS. For some reason EnableNetworkFSS is not set here.
To disable CPU fair sharing in PowerShell you write.
$temp = (gwmi win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices")
$temp.enableDFSS = 0
$temp.put()
To disable disk fair sharing in PowerShell you write.
$temp = (gwmi win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices")
$temp.enableDiskFSS = 0
$temp.put()
To disable network fair sharing in PowerShell you write.
$temp = (gwmi win32_terminalservicesetting -N "root\cimv2\terminalservices")
$temp.enableNetworkFSS = 0
$temp.put()